The determination of HBA1C has several advantages over blood glucose, but its exclusive use may present problems, this being the issue that the authors deal with in this article.Instead of being a step forward, taking a step towards HBA1C as a diagnostic method could be too far.
At present, diabetes is diagnosed by measuring the concentration of plasma plasma on an empty stomach (7 mmol / l threshold) or after an oral glucose tolerance test (11.1 mmol / l).However, an International Expert Committee composed of members designated by the American Diabetes Association, the European Association for Diabetes Study, and the International Diabetes Federation recently recommended that these tests are replaced with an analysis of glycosylated hemoglobin A1C(HBA1C).
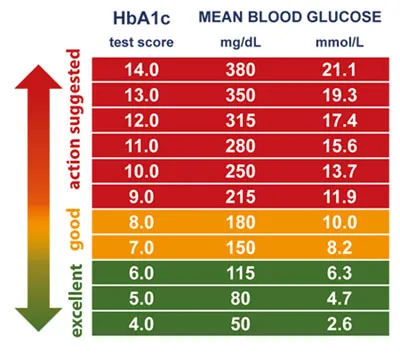
The Committee declared that any person with a confirmed HBA1C value of 6.5% (48 mmol / mol) is made without glucose tests, although glucose criteria will continue to be used in people in whichThe HBA1C measurement can be inadequate.The determination of HBA1C has several advantages over blood glucose, but its exclusive use may present problems, this being the issue that the authors deal with in this article.
Advantages of hemoglobin A1c.
The expert committee document did not give specific reasons to dispense with the criteria of glucose in favor of HBA1C, but it does highlight many of the advantages of the use of HBA1C.
These include the undoubted advantages of requiring a sample of blood and of being able to determine glycemia outside the state of fasting.
The daily variability of HBA1C in an individual is also less than that of fasting glucose and considerably lower than the glucose concentration after a glucose tolerance test (coefficient of variation of 3.6% V 5.7%V 16.6% in a study), so that repeated measurements must be more consistent with HBA1C.
There is also the argument that, when obtaining an estimate of blood glucose during the previous weeks or months, HBA1C could provide a more complete vision than the measurement of blood glucose in a single sample on an emptyics or with the "artificial" conditions of aglucose tolerance test, to which the expert committee refers as the justification of "common sense" for use.The determination of HBA1C is also the most common means for the management of diabetes and treatment adjustment, so its use for diagnosis would simply be an extension of this function.
Advantages glycemia fasting
-Stable as the current diagnosis of diabetes.
-Mid directly the molecule that is considered to cause the complications of diabetes.
-It is not subject to deceptive results due to non -glycemic factors.
-The differences in laboratory results are smaller than among the results of HBA1C.
-Your determination is more accessible than that of HBA1C worldwide
Disadvantages Glycemia in fasting
-Rere that the patient is fasting and that the sample is promptly analyzed.
-It can require a glucose tolerance test for the diagnosis of diabetes.
-A only glycemia can have greater variability than HBA1C.
-The glucose tolerance test can be unrealizable in patients with gastric surgery.
Advantages Hemoglobin A1c
-Stable for the monitoring of patients diagnosed with diabetes.
-I don't require an empty show and after collecting the sample is more stable than glucose.
-Lime control the glucose level in the previous weeks or months.
-Individual variability lower than the variability of glucose. Hemoglobin disadvantages A1c
-The result can be misleading in patients with hemoglobinopathies, anemia, renal failure or may differ among patients of different ages and ethnic origin.
-Mayores differences in the results between laboratories.The cost restricts access to the test in many geographical regions.
-It is an indirect marker of hyperglycemia with discrepancies between individuals and between glucose and HBA1C.
A previous obstacle to considering the use of HBA1C for diagnosis has been the lack of standardizations for the test, which means that the results could vary depending on the laboratory method used.This is being overcome through the standardization led by the International Federation of Clinical Chemistry and Clinical Laboratory.
Disadvantages
The case of moving to HBA1C as a diagnostic method seems convincing.However, there are some real difficulties.In fact, the expert committee accepts many of the problems inherent in the use of HBA1C for diagnosis but does not speak of the possible practical effects of these limitations.For example, the presence of abnormal hemoglobin can affect the measurement of HBA1C and give false results.Therefore, the result depends on the analyzer used.An analyzer could identify and account for certain hemoglobinopathies but not others, and another different analyzer could collect (or lose) a totally different spectrum of abnormal hemoglobins.
The prevalence of hemoglobinopathies varies greatly between countries and races;A measure of the magnitude of the problem is to arise from the observation of the population of the United States, with the presence of the anemia of falciform or hemoglobin Cells C. at least, 10% of the 26 million African -American citizens are the bearer of theseHemoglobinopathies and may have incorrect results in, which can give false results in almost a third of HBA1C analyzers that are usually used in that country.Therefore, the authors say "are we going to be sure that someone does not have a hemoglobinopathy that is generating or discarding a diabetes diagnosis properly?"
When glucose measurements are discrepant with the results of HBA1C, when the result of HBA1C is unexpected or greater than 15%, or when the value changes drastically after a change in the laboratory method in patients with diabetes already diagnosed, National Health Institutes of the United States recommend considering the possibility of hemoglobinopathy in African, Mediterranean people, or southeast Asia.But if HBA1C is the only means of diagnosis and glycemia automobile is not promoted until diabetes becomes an required insulting, patients can be identified erroneously, without additional expenses and interpretations, and the consent required forthe detection of concurrent abnormal hemoglobin.
Iron deficiency anemia (a condition that affects 3.3 million American women) can also increase HBA1C by 1-1.5% with respect to the usual figure before iron treatment. ”Should studies be done to diagnose theFerropenic anemia such as hemolytic anemia and any other condition that can alter the survival of erythrocytes in any person with suspected diabetes? ”“What happens to patients with renal failure, which can have a variable effect on HBA1C concentrations (through hemolysis, iron deficiency, carbamylated hemoglobin formation) and diseases such as HIV, inwhich HBA1C is 1% lower in patients who take antiretroviral drugs?
HeCommittee mentions the effect of aging (HBA1C is 0.4% higher in those over 70 years compared to 40 -year -old people with the same glucose tolerance) 10 and ethnic origin (0.4% higher inAfro -Caribbeans that in Europeans), but considers that "their etiology and meaning are not clear." So, meanwhile it does not know it is possible to make an erroneous diagnosis in the study of diabetes in older and non -European people.In fact, the Commission does not take into account if individual variability in the relationship between the HBA1C concentration and the mean of blood glucose is important.
Even the passage to standardization of HBA1C measurement, although necessary, does not instantly improve the results of the analysis.This was demonstrated in June 2009 when the UK National External Quality Assessment Service of the United Kingdom found that 251 laboratories sent standard samples with an HBA1C concentration of 6.5% reported values that range between 5.8% and 7.2%.The variation could be even greater in countries with less resources for the measure of HBA1C and less experience with the homogeinization of methods.These issues to ensure its accuracy and the potential list of necessary evidence, in addition to the determination of HBA1C, make the idea of simply fasting since the eve of a blood glucose is much more attractive.
The objective of the diagnosis of type 2 diabetes is to identify people at high risk of developing microvascular complications of the disease.As HBA1C will identify diabetes in different groups of people that identifies glycemia, there is still concern in what is the extent to which HBA1C can predict microvascular risk, compared to glycemia, even after excluding people inThose that HBA1C measurement can pose a problem.
The main figure in the expert committee report shows 3 studies (in the Pima, Egypt Indians, and US populations.postprandial and the HBA1C levels that are around the same decil, which implies that the tests are interchangeable.However, this would be expected in a population regardless of how bad predictor is a risk prediction test compared to another.What is not mentioned is that all participants of the 3 studies show that the characteristic curves of the operation of fasting blood glucose or 2 hours postprandial are better than HBA1C.A study cited to justify 6.5% of HBA1C showed that random blood glucose always gave "similar results."The report presents new data (not yet published in its entirety) that show that HBA1C is at least as predictive retinopathy as blood glucose.
Before considering any change, you should also know the current WHO recommendation to measure the glucose of 2 hours in patients with alteration of fasting glycemia results, as practiced in many countries;It is only compared to the measurement of fasting glycemia or HBA1C.On the other hand, in large studies of the HBA1C in the population it is usually measured by the same method, or even the same instrument, in a central laboratory.This eliminates the differences between the laboratory HBA1C results and can give a false impression of how well the test is carried out routinely.
Finally, the HBA1C cut point is 6.5%.It is likely that any limit is to some extent arbitrary, but a proposed objective for the use of HBA1C is to help reduce the time between the appearance of diabetes and diagnosis and to capture the third of patients who have diabetes but notThey know.However, they sayThe authors, according to data from the US National Health and Nutrition SurveSo, the use of an HBA1C threshold of 6.5 %, will add third missing patients.What this probably means is that in people for whom the measurement of HBA1C is not very reliable, the use of glycemic criteria 2-3 times more likely to be diagnosed as diabetics than in whom the determination has been usedof the HBA1C.There is also the problem of diagnosing diabetes in person with 10 mmol / L fasting glymia, and an HBA1c test of 6.4% (47 mmol / mol).
Conclusion
When new diagnostic criteria for any disease are proposed, they are supposed to be clearly higher than the criteria in force.There are advantages and disadvantages for the use of glycemia or HBA1C as methods the diagnostic diagnosis.However, blood glucose can present less risk of a bad complete diagnosis than the measurement of HBA1C alone.Instead of being a step forward, taking a step towards HBA1C as a diagnostic method could be too far.