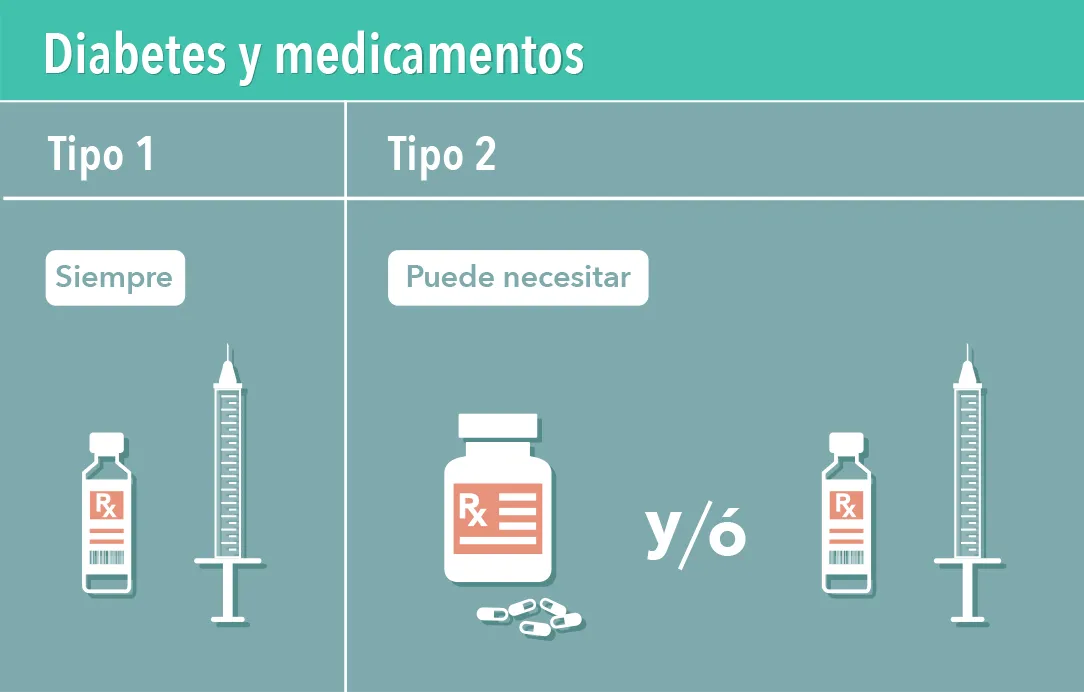
In type 2 diabetes, treatment with pills is often insufficient, so it is usual to also introduce insulin injection.
For the patient this moment turns out to be conflictive, because it is perceived as a certain failure or worsening of their diabetes, which is why it tends to delay, often, more than necessary.
But ... what happens when the pills are no longer enough to control glucose?
Blood glucose levels begin to rise, with the consequent real worsening of health, in addition to the appearance of complications derived from a treatment that does not cover the real needs of the body.
For this reason, it is not a failure to use insulin in type 2 diabetes, it is a necessary evolution to maintain our controlled glucose levels.
You could say that insulin in our body works in two ways.
a) The insulin in bolus that is used to cover the amount of food that is going to consume mainly carbohydrates as well as to make glucose corrections that is, lower blood glucose when it is high.Know more about insulin for bowling, here.
b) The basal insulin that bears that name because it works as a base regardless of the foods consumed.Basal insulin is that our body requires to regulate all these glucose variations that have nothing to do with food but with hormonal, physiological, etc.The objective of this type of insulins is to regulate glucose
What are the basal insulins found in the market?
The objective of this type of insulins is to meet insulin requirements between meals, we can find them as follows:
Intermediate or NPH: Insulatard;NPH Humulin
Prolonged: Gliargine (Absaglar, Lantus, Toujeo);Deteminr (Levemir);Swallow (Tresiba)
Basal insulins have an action of 1 to 2 hours except the toujeo whose beginning is between 3 and 4 hours, they have a very light peak that is not considered except for the NPH whose maximum peak is at 4 to 48 hours after application and its duration ranges from 12 hours in the case of NPH until 42 hours in the case of Degludec insulin.
When will a doctor prescribe insulin use?
According to the care standards of the American Diabetes Association, doctors are recommended to consider basal insulin to people with type 2 diabetes when:
- There is a continuous weight loss.
- There are symptoms of hyperglycemia.
- When A1C levels are greater than 10% (86 mmol/mol).
- Blood glucose levels are very high (greater than 300 mg/dl).
However, if despite already administering basal insulin, the A1C remains above the objective, a doctor can prescribe insulin in bolus to complement with food intake.
How to use basal insulin?
The doctor will tell you which insulin as well as the amount of insulin you require.The dose is personalized and the dose of another person should not be used.For more information we share information about insulin injection methods as well as know how to apply insulin.
What are the risks and advantages of applying basal insulin?
The main risk when using insulin is hypoglycemia or low blood sugar is increased especially if the physical activities to which it is accustomed such as walking a little more or performing a more intense exercise or, apply more insulin is changedthan recommended.
However, this can be seen by the use of glucose monitoring to know the behavior of glucose throughout the day.Know more about hypoglycemia and how to prevent them if they happen.Otherrisk is omitting or not applying less insulin than the indicated one which leads to a blood glucose elevation
The advantage of the insulin application is to achieve a better handling of our glucose with a longer time in rank and the decrease in the presence of complications of diabetes.The disadvantage would be the injections that would be required to apply insulin.
Key points:
- Basal insulin is one that our body requires to regulate all these glucose variations that have nothing to do with food but with hormonal, physiological, etc.
- Your start time can vary from 1 to 4 hours.
- Its maximum action peak goes from 4 to 8 am or have a minimum action peak.
- Its duration ranges from 12 to 42 hours.