Diabetes is a pathology that increasingly affects more people worldwide.According to data from the World Health Organization (WHO), the number of people with diabetes has increased from 108 million in 1980 to 422 million today.
On the other hand, it is important to keep in mind that the prevalence of diabetes has increased more quickly in medium and low -income countries.
It is a disease that occurs as a consequence of the lack of blood sugar level control, a value that is known as glycemia.Insulin, which is the substance secreted by the pancreas, is responsible for performing this task, but in the case of diabetic patients it cannot do so, either because the pancreas does not secretly in sufficient quantity or does not do so in any way.Thus, the low amount of insulin in the organism - or null - causes glycemia out of control and the person has the level of high blood sugar constantly.
Although its direct consequence is reflected in the blood, diabetes can cause severe adverse effects on patient's health.
A person suffering from this disease may experience various consequences in his body in the short term.In general, they occur after acute decompensation of the disease, regularly related to the lack of control of it or inconvenience with medication.
ketoacidosis
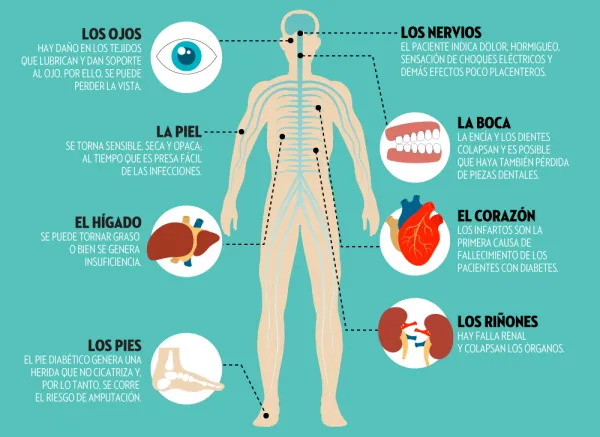
It is a serious condition that can also produce a diabetic coma and even death.When the cells are not receiving the glucose they need as a source of energy, the body begins to burn fat to have energy, which produces a harmful chemical reaction -considering ketones.The body does this when it does not have enough insulin to use glucose, the normal source of energy of your body.When ketones accumulate in the blood, they make more acidic, which constitutes a warning signal that diabetes is out of control.
Ketoacidosis can be presented in any person with diabetes, although it is rare in people with type 2 diabetes. Some older people with type 2 diabetes may have a different serious condition, called non -ketosic hyperosmolar coma, in which the body tries to get rid ofof excess glucose by urine.
The treatment of ketoacidosis generally requires hospitalization.
diabetic coma
It is a complication of diabetes that puts life at risk and produces loss of consciousness.The dangerously high levels of blood sugar -hiperglycemia- or dangerously low blood sugar levels - hypoglycemia - can cause a diabetic coma.
Faced with a situation of these characteristics, the consultation with a doctor immediately is important, since the patient's life may be at risk.
On the other hand, diabetes can also cause long -term consequences, especially in patients who do not control properly and do not follow treatments as specialists indicate.Some milder than others, for patients suffering from this pathology, it is important to know them in order to treat them in case they appear.
kidney disease
Nephropathy is much more frequent in people with diabetes than in those who do not have it.In this sense, diabetes is constituted as one of the main causes of chronic kidney disease.The cause of this pathology is a deterioration of small blood vessels, which can make the kidneys less efficient, or to fail completely.
cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease is the most common cause of death and disability among people suffering from diabetes.The angina on chest, the infarction ofMyocardium, stroke, peripheral arterial disease and congestive heart failure are the most intimately associated pathologies associated with diabetic patients.
In turn, hypertension, hypercholesterolemia and hyperglycemia are three of the risk factors that can contribute to the risk of cardiovascular complications.
ocular disease
According to the specialists, most people who have diabetes will develop some form of ocular disease -retinopathy- at some point in their lives.If the patient, in addition, has high blood pressure and cholesterol, is more likely to suffer from some type of ocular pathology.
Retinopathy is a disease that occurs by blocking or damage of the network of blood vessels that feeds the retina, which can cause loss of vision permanently.
complications during pregnancy
Women with any type of diabetes run the risk of developing complications during pregnancy if they do not undergo frequent checks.Hyperglycemia during pregnancy can cause changes in the fetus, which in turn can cause problems during childbirth or baby injuries during birth, for example.Children who are exposed to hyperglycemia in the uterus for a prolonged period run a greater risk of developing diabetes in the future.
nerve injuries
The results of a neuropathy - provocated by high blood glucose and blood pressure - can be diverse according to which nerves affect.Problems in digestion, urinary or impotence incontinence can be some of the adverse effects related to the disease condition by diabetes.However, it is important to note that the most affected areas are the limbs and, more precisely, the feet.Known as peripheral neuropathy, they can generate pain, tingling and loss of sensation, which can be especially harmful, since the lesions can go unnoticed and trigger in serious infections, diabetic foot or amputations.
oral health
Traditionally it has not been considered a complication, but in recent years the specialists have indicated that diabetes can be a danger to the health of the mouth and teeth.It is very common for diabetic people to develop gingivitis -inflamation of gums-, for example.In turn, gingivitis is the main cause of loss of dental pieces.